Know Your Customer (KYC) in BrokerTools

Introduction
Fair Trading Technology’s BrokerTools is a comprehensive suite of trading software and services designed for brokers. One of the key features offered in BrokerTools customer onboarding process is Know Your Customer (KYC). This is a procedure that helps brokers to perform KYC on their new customers and identify and mitigate fraud.
The KYC regulations are a critical component of any broker’s compliance program. They enable the verification of customer identities and the collection of information about customers’ financial backgrounds. This information is particularly crucial to assess the customer’s risk profile and prevent money laundering, financial crimes, and other fraudulent activities..
Fair Trading Technology’s KYC is streamlined and automated process for customer identity verification and risk assessment. It uses a variety of data sources such as:
- Primary source data: official government sources (credit bureaus, land registries etc.), corporate registries, and other publicly available resources,
- Anti-money laundering (AML) databases and data sources: embargo and sanctions programs, regulatory and law enforcement watch lists.
What are the benefits of using KYC technology?
Know Your Customer section offers many benefits to brokers, and the most important ones are:
- Enhanced compliance: Implemented compliance system helps brokers to comply with KYC regulations. The system ensures that brokers collect the required information from their customers and that they assess customer risk appropriately.
- Reduced risk of fraud: By using a variety of data sources and algorithms to assess customer risk, brokerage companies easily identify and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Data protection: Customer data is one of the most valuable assets of brokerage companies. KYC solutions provide an additional level of security to prevent any third parties from accessing the customers’ accounts.
How does the KYC process work in BrokerTools?
Know Your Customer section in BrokerTools could be viewed as a four-step process:
- Customer onboarding: When a new customer opens an account with the broker, they are required to provide certain information. This includes information like their name, address, date of birth, and personal ID number. Besides ID (identification card) or passport, documents for customer data verification could include company incorporation documents. Documents like bank statements, receipts (transaction proofs) or recent utility payment bills to validate the addresses where customers are located. The broker also collects information about the customer’s financial background. These inculde their source of funds and their investment experience.
- Document verification: Then the broker verifies the customer’s identity and financial information by reviewing copies of the customer’s government-issued ID, bank statements, and other documents.
- Risk assessment: Information collected from the customer onboarding and document verification steps are used for assessment of the customer’s risk profile. This assessment considers a variety of factors, including the customer’s country of residence, type of account, trading history, and sources of funds.
- Decision making – approval or rejection of customer: The final step in developing a customer’s risk score is when the broker determines whether to accept the customer as a client and set the customer’s trading limits.
Know Your Customer section configuration in BrokerTools
KYC configuration in BrokerTools enables brokers to quickly and easily set up and manage key configuration options for new customer’s data by:
- Adding risk classification with defining rule sets and risk rating per customer’s country of residence,
- Editing rule sets through:
- KYC steps – defined steps and priorities in KYC checklists, that brokers can perform in their standard check procedures.
- Required documents – listed documents (mandatory, or not) included in check procedures,
- KYC fields – defined fields from customer’s address details, customer’s trading and investing experience (shown in years, and amounts of invested money in recent 12 months), and defined field for KYC review, that gives broker options to approve or reject customer.
- Extended registration order – set order of necessary parts from adding KYC fields, approving Terms and Conditions, creating wallet, to performing external KYC verification.
- Supported countries – creating separate rules for different countries.
- KYC automation – enabling KYC-prequalification and external KYC verification via 3rd party KYC providers such as IDWise, Idenfy, GBG, SumSub among others.
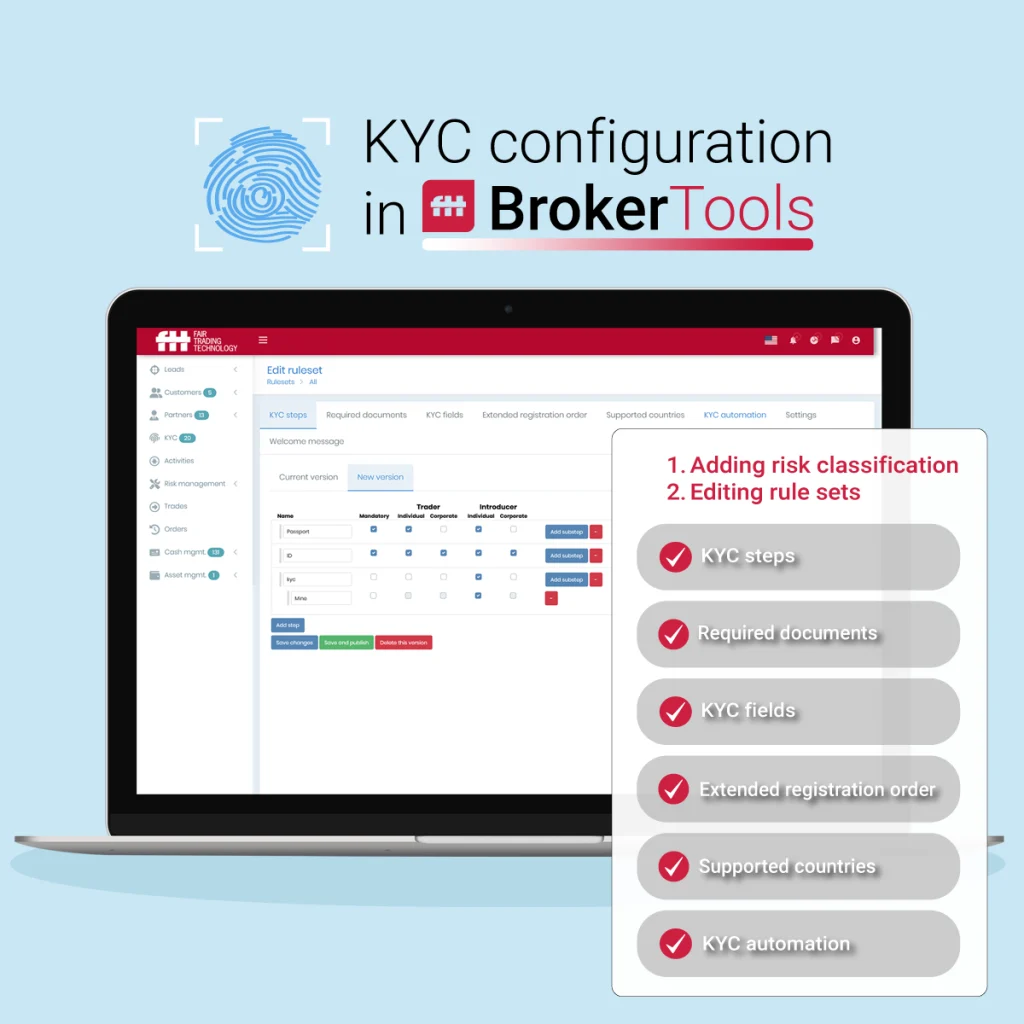
BrokerTools Know Your Customer section configuration offers brokers a plethora of options to include in the KYC process. Thereby it’s serving as a solid base for customer profiling. For instance, an example of using KYC is the customer signup form that brokers can set up in BrokerTools. Through this form, they can immediately acquire initial data about the customers.
Best practices for using the KYC in BrokerTools
To get the most out of the KYC, brokers should follow these best practices:
- Keep the system up to date: System should be updated regularly to reflect changes in KYC regulations and to include new data sources.
- Use all the data sources: Variety of data sources are recommended to be used to verify customer identities and assess customer risk. Brokers should use all the available data sources to get the most complete picture of each customer.
- Review the system regularly: Brokers should regularly review the KYC to ensure that it is working properly and that it is being used effectively. In this case, alongside brokers KYC provider companies can be very supportive and advisory in reviewing the system.
Conclusion
Fair Trading Technology’s Know Your Customer is a powerful tool that can not only help brokers to identify and assess potential risks associated with their customers but also enables them to make informed decisions. Decisions about engaging in opening accounts, starting business transactions, and providing financial or any other services to customers. As a result, the Know Your Customer section intrinsically builds up and maintains a regulatory compliance system. It also mitigates business risks, helps to prevent fraud, and generally safeguards brokers’ reputation. In essence, it is a secure framework for responsible and ethical business practices in the industry nowadays. It is a condition that is unmistakably required in modern financial markets.